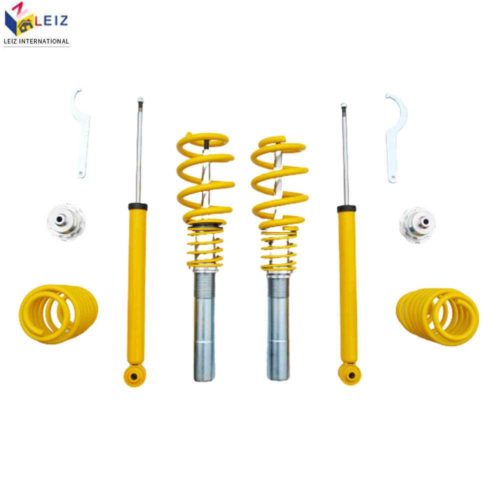
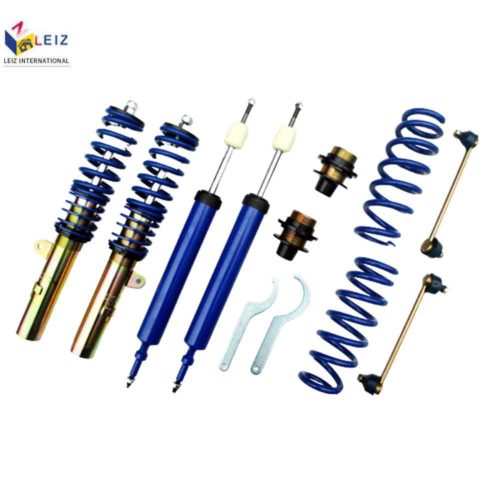
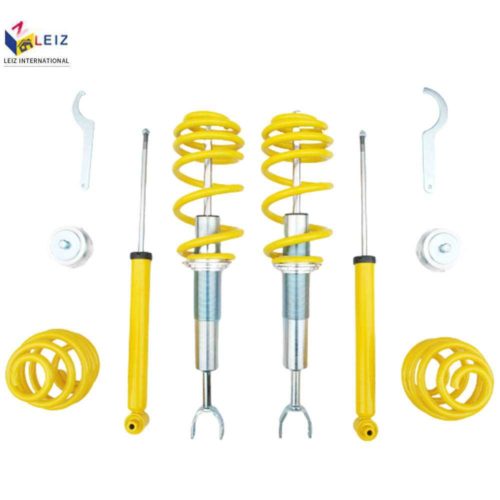
Description
The function of Hydraulic shock absorber
Hydraulic shock absorber relieves the road surface’s impact and quickly absorbs the vibrations caused by bumps, allowing the vehicle to return to its normal driving condition.
In the event of damage to the damper, a case-by-case analysis is required.
1. In functional failure, the inability to absorb vibration will increase the number of vibrations.
2.An oil or air leak will result in a thumping noise when the vehicle crosses a pothole and feels that the vehicle has no cushioning.
A simple way to determine this.
1. Press down on the boot with your hand and release it. The vehicle is considered normal if it stops within 3 vibration cycles; otherwise, it is recommended to be checked.
2. Lift the vehicle and check the appearance of the damper. If there are any visible oil stains (usually more than 1/2 of the total length), it is recommended to consult a service technician for replacement.
Note: A clear distinction should be made between oil and water stains, and replacement is not recommended if there is no problem with the damper.

What is the working principle of the Hydraulic shock absorber?
The Hydraulic shock absorber is used to dampen the vibrations and impacts from the road surface when the springs bounce back after absorbing the vibrations. It is widely used in automobiles to accelerate the decay of bai vibrations in the frame and bodywork in order to improve the smoothness of the car’s ride. When passing over uneven surfaces, although the shock-absorbing springs filter the vibrations from the road surface, there is a reciprocating motion of the springs themselves. The Hydraulic shock absorber are used to suppress this spring jump.
Suspension system due to the impact of the elastic components to produce vibration, in order to improve the smoothness of the car, suspension and elastic components in parallel with the installation of shock absorber, for attenuation of vibration, car suspension system with Hydraulic shock absorber is mostly hydraulic shock absorber; its working principle is that when the frame (or body) and the axle between the vibration and relative movement, the piston in the shock absorber up and down, shock absorber cavity fluid repeatedly from the oil to the oil in the piston. One chamber flows into the other through different pores. The friction between the pore walls and the oil and the internal friction between the oil molecules forms a damping force on the vibrations, which transforms the vehicle’s vibration energy into oil heat energy, which is then absorbed by the Hydraulic shock absorber and distributed to the atmosphere. The damping force increases or decreases with the relative speed of movement between the frame and the axle (or wheels) and is related to the viscosity of the fluid, provided that the fluid channel cross-section and other factors remain unchanged.
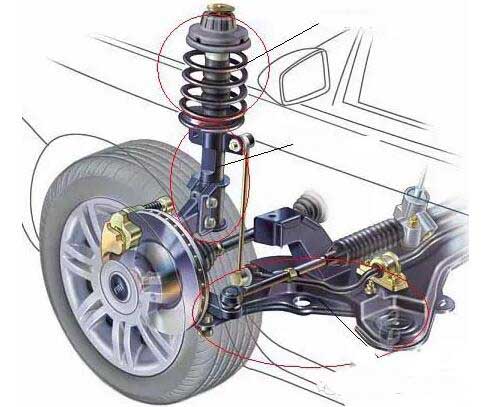
Shock absorbers and elastic elements are responsible for shock mitigation and damping, and excessive damping forces can deteriorate the suspension’s elasticity or even damage the shock absorber connections. This contradiction between the elastic element and the Hydraulic shock absorber must, therefore, be adjusted.
(1) During the compression stroke (when the axle and frame are close to each other), the shock absorber’s damping force is low to give full play to the elastic element’s elastic action and to soften the impact. In this case, the elastic elements play a significant role.
(2) During the stretching of the suspension (the axle and frame are far from each other), the shock absorber’s damping force should be high so that the shock is damped quickly.
(3) When the relative speed between the axle (or wheels) and the axle is too large, the dampers are required to automatically increase the fluid flow so that the damping force is always kept within certain limits to avoid excessive shock loads.
The car suspension system is widely used in the cartridge dampers. In compression and extension can play a damping role in the stroke called double-acting dampers; there are new dampers, including inflatable dampers and adjustable resistance dampers.

Description of the double-acting cartridge dampers’ working principle: During the compression stroke, the piston in the damper moves downwards as the car wheels move closer to the car body and the damper is compressed. The volume of the piston’s lower chamber decreases, the oil pressure rises, and the oil flows through the flow valve to the chamber above the piston (upper chamber). The upper chamber is partly taken up by the piston rod. The upper chamber’s increased volume is less than the reduced volume of the lower chamber, and part of the oil then flows back into the reservoir by pushing open the compression valves. The saving of oil by these valves creates a damping force for the compression of the suspension. The dampers are stretched during the extension stroke, with the wheels moving away from the body in equivalent proportions. At this point, the piston of the damper moves upwards. The oil pressure in the piston’s upper chamber rises, the flow valve closes, and the oil in the upper chamber pushes open the extension valve and flows into the lower chamber. Due to the presence of the piston rod, the oil flowing from the upper chamber is not sufficient to fill the increased volume of the lower chamber, and a vacuum is created in the lower chamber, which is replenished by the oil in the reservoir by pushing open the compensating valve 7. Due to the throttling action of these valves, the suspension is damped during the extension movement.
As the spring stiffness and preload of the extension valve are designed to be greater than that of the compression valve, the sum of the channel loading areas of the extension valve and the corresponding average gap is smaller than the sum of the cross-sectional areas of the compression valve and the corresponding average gap under the same pressure. This makes the damping force generated by the damper’s extension stroke more significant than the damping force of the compression stroke, thus meeting the requirement for rapid damping.

Specification of Hydraulic shock absorber Model No.LZ-ABM1002
Pls contact us for more information about Hydraulic shock absorber
Related products




