What Is DDP?
![]() Leiz International performance as a professional B2B suppliers based in Shanghai,China,to provide clients what they need exactly
Leiz International performance as a professional B2B suppliers based in Shanghai,China,to provide clients what they need exactly
![]() Leiz International provides full services for our clients from the get the products information to arrange the shipment to the destinations.
Leiz International provides full services for our clients from the get the products information to arrange the shipment to the destinations.
![]() Leiz International is familiar with export and import matters, and also have enough experiences to help clients make the B2B orders.
Leiz International is familiar with export and import matters, and also have enough experiences to help clients make the B2B orders.


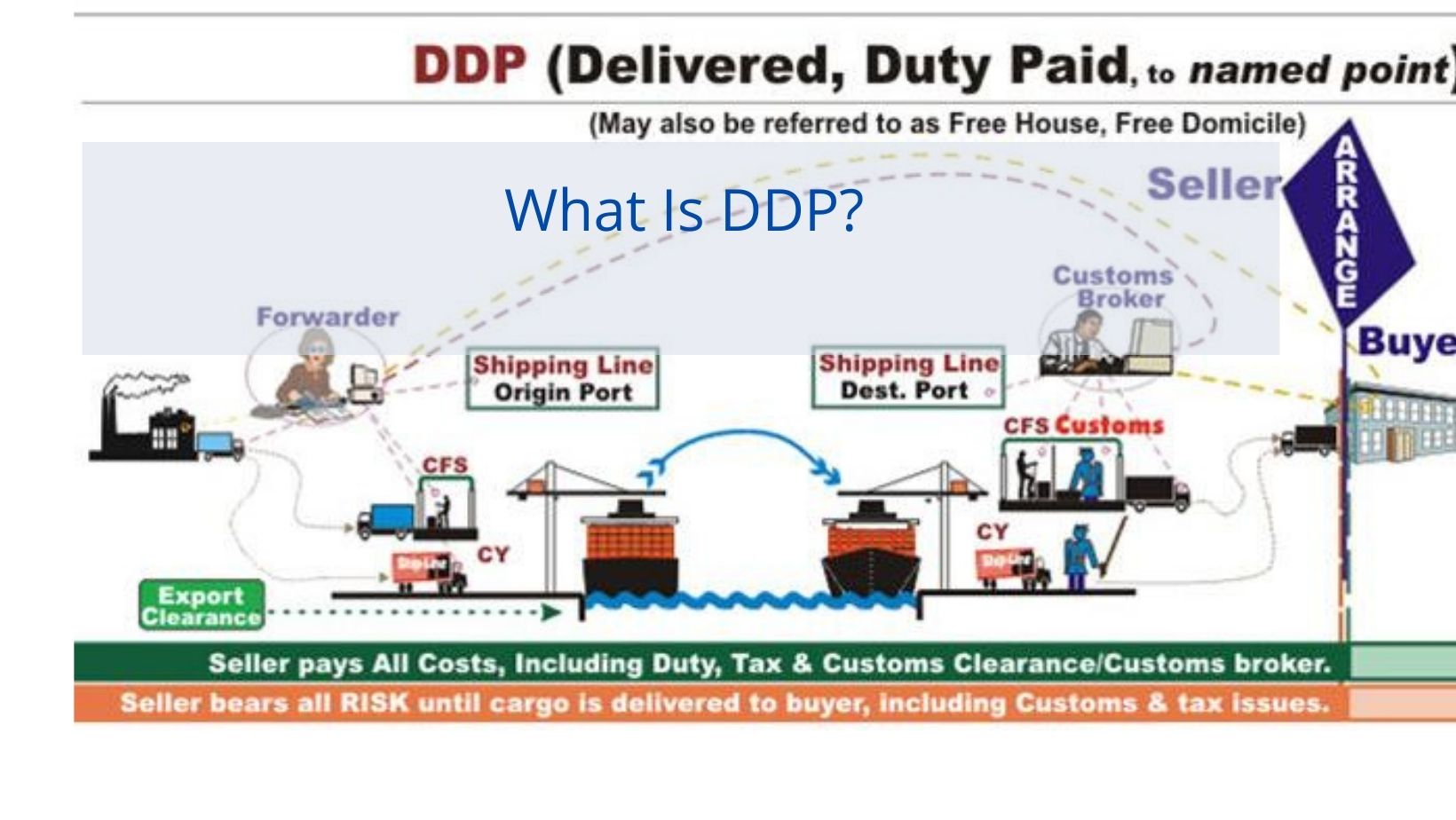
What Is DDP?
DDP
Duty Paid (…… Designated Port)
“Duty Paid (…Designated Destination)” means that the Seller completes import customs clearance at the designated destination and hands over the unloaded goods on the delivery vehicle to the Buyer to complete the delivery. The Seller must bear all risks and costs of transporting the goods to the named destination, including any “duties and taxes” paid at the destination when customs formalities are required (including the responsibility and risk of customs clearance and the payment of handling charges. Tariffs. Taxes and other charges).
17 Important Tips For You If You Are Importing Products From China
The best way is to have an agent in a reliable port to get a complete document and go to customs for delivery.
DDP seller’s obligations.
The obligations of the Buyer and Seller under DDP.
Supply of goods by the contract.
To supply merchandise and commercial invoices consistent with the sales contract and such other documents as may be required by the contract to prove that the goods conform to the contract, by the provisions of the sales contract.
A2. Licenses. Approval certificates and customs formalities.
Self-supporting, self-financing, obtaining import and export licenses or other official approval documents, and handling all customs formalities necessary for the export and, if necessary, transit transportation of the goods through other countries.
III. Contract of carriage and insurance contract.
a) Contract of carriage.
At own expense, the contract of carriage of goods to an agreed place, under the customary practice of transporting the goods to the specified destination under the customary practice. If the specified delivery point is not agreed upon or is customarily uncertain, the Seller may choose the most suitable place at the specified destination.
b) Insurance contract.
There is no obligation to enter into an insurance contract.
A4. Delivery
The Buyer will use the goods on the date and within the period specified in paragraph A3.
5. Passing of risk.
All risk of loss of or damage to the goods shall be assumed until delivery of the goods under item A4, except in the cases described in paragraph B5.
A6. Allocation of Costs.
Except in the circumstances described in paragraph B6.
(a) Pay all costs, other than those arising under paragraph A3, until delivery of the goods following paragraph A4.
(b) Unless otherwise agreed, payment of all customs formalities required for export and import of the goods and all duties payable. Contributions and other official fees and, if required, all charges required to transit the goods through another country before delivery of the goods under paragraph A4.
7. Notification to Buyer.
Provide Buyer with adequate notice that the goods have been dispatched and advise Buyer whether to take such other notices as may generally be necessary to accept the goods.
Delivery note. Shipping documents or corresponding electronic documents.
The Buyer submits at its own expense the bill of lading and the ordinary transport document requested by the Buyer to collect the goods (e.g., negotiable bill of lading. Non-negotiable sea waybill. Inland waterway bill. Airwaybill. Rail consignment note. Road consignment note, or multimodal waybill).
If the Buyer and Seller agree to use electronic communications, the previously mentioned documents may be replaced by equivalent electronic data (EDI) documents.
9. Verification. Packaging. Marking.
Payment for verification of goods delivered under paragraph A4 (e.g., quality inspection, metering, weighing. Point). Provide, at your own expense, the packaging required for the concert goods (except for special industries, delivery of contract goods generally does not require packaging). The packaging shall be properly marked.
10. Other obligations.
Payment of all costs incurred in obtaining the documents referred to in paragraph B10 or equivalent electronic documents and reimbursement of costs incurred by Xi in assisting.
At the Buyer’s request, provide the information required for insurance purposes.
How To Find Your Reliable China Wholesale Suppliers For Long-Term Business?
The obligation of the Buyer under DDP
B1. Make the payment.
Payment is made following the contractual payment method.
B2. License. Approval of certificates and customs formalities.
At the Seller’s request and the risk and expense of the Seller, all assistance is given to the Seller in obtaining the necessary licenses or other official approval documents for the importation of the goods.
B3.Contract of carriage.
There is no obligation to conclude a contract of carriage.
B4. Collection of goods.
When the goods have been placed following paragraph A4, they shall be collected immediately when used.
5. Passing of risk.
Assumes all risk of loss or damage to the goods from the time they are placed at its disposal by paragraph A4.
If Buyer fails to give notice following paragraph B7, it assumes all risk of loss of or damage to the goods, i.e., the goods have been placed at its disposal as of the date of expiration of the agreed date or period for which delivery has been made as specified, in the sense that the goods have been assigned to this contract, i.e., the goods have been supplied under this contract as expressed or otherwise.
B6.Cost Allocation.
All charges for the Goods shall be paid when the Goods are placed at its disposal by paragraph A4.
Suppose Buyer does not accept the goods by paragraph A4 or fails to notice paragraph B7. In that case, Buyer does not accept the goods and bears all additional costs arising from that place, provided that such goods have been duly placed at its disposal hereunder, that is, to the extent that the goods have been expressly allocated or otherwise identified as supplying the goods hereunder.
B7. Notice to Seller.
Adequate notice shall be given to the Seller when Buyer has the right to determine the time and place of receiving the goods at the specified time.
Delivery Note. Shipping documents or equivalent electronic documents.
Acceptance of the bill of lading or shipping documents following clause A8.
How To Arrange Shipment From China To USA
9. Cargo Inspection.
Unless otherwise agreed, the cost of inspection of the goods before shipment is enforced by the competent authorities of the exporting country.
B10. Other obligations.
At Seller’s request and risk and expense, give Seller all assistance in obtaining any documents or equivalent electronic documents required by Seller that are placed at Buyer’s disposal by the importing country under this term.
Why do buyers choose DDP?
The main reasons why customers choose DDP terms are as follows.
The customer initially or just started importing and does not know enough about transportation, customs, etc., so he relies on the exporter to help him deal with these aspects.
Other customers, especially some French customers, do not want to do this kind of thing, so they push the exporter to do it.
In addition, some customers do DDP to reduce the risk of importation, especially for certain goods that are vulnerable to import restrictions, tariffs, or trade barriers. The risk is transferred to the exporter through the DDP clause.
For exporters, DDP has risks.
First, DDP poses a greater risk to the Seller than FOB/C&F and should be considered the riskiest trade terms. Under FOB or C&F, the risk is transferred to the Buyer when the goods are loaded on board. However, under DDP, the Seller’s risk remains until delivery to the customer. If there is any mistake in the goods, the Seller pays for it all. Therefore, if the Seller does DDP, it is better to apply for cargo transportation insurance to find the insurance company if there is any problem.
Second, for FOB/C&F, DDP sellers must understand the importing country’s customs or other government departments on the policy of such goods, whether there are any restrictions, whether the need for certification, how much the import tax. The goods arrive at the port of destination and then go through, then you have to know first, it will be very troublesome. For example, for food going to the U.S., it is equally important to know the terms of the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) in addition to the U.S. Customs tariff.
Again is the offer, DDP involves a lot of links, there may be some links in the initial costing did not take into account, for example, the port of destination customs inspection of goods generated by inspection costs, even after the stacking fees, there are some other links to generate additional costs. So in the cost of customer quotes for re-accounting, it is best to leave more room for costs unrelated to COVER.
How to reduce the risk of DDP exporters How to reduce the risk of DDP exporters? The following points should be noted.
Firstly, as mentioned earlier, buy a warehouse to warehouse cargo transportation insurance to avoid accidents in transportation.
Second, find an experienced and strong forwarding company because DDP involves very high costs, such as inexperienced freight forwarders, then report errors. Otherwise, it will cause losses. When the shipper inquires the forwarder, the condition of the goods should be confessed, especially the name of the goods; please provide Chinese and English (material, use, model) customs codes. Generally, the first six can be, as the last four different countries HS CODE is different, the specific address and postal code, FOB value, and so on.
DDP has benefits for exporters.
Ordinary DDP this payment terms, exporters can make a fortune, and exporters favorite. But few customers are willing to do this; most still want to do FOB or CIF.
Whether it is DDP sea or air, it lets the foreign agent help customers clear customs. On behalf of the customs duty, pay the inland freight to send the goods to the customer’s designated warehouse. This is a large number of miscellaneous fees; the cost becomes opaque; you can also cut prices with the freight forwarder and then the guest side to earn a little more difference, plus the product’s profit is very good.
Payment method under DDP
If the trade terms are DDP, there are two payment methods; one is 100% of the former T / T, the other is OPEN ACCOUNT. To put it plainly, DDP is the exporter to send the goods to the foreign customer’s warehouse before all the costs are paid by the exporter, the exporter handles all procedures, all the risks are borne by the exporter.
If it is the first time to do DDP with customers, it is best to ask customers to pay 100% in advance.
Which countries prefer using DDP?
The countries where we have operated more DDP shipments are the USA, Europe (among European countries, France is the most preferred country to use DDP), and Russia. Russia is a special case because, in the past, many shipments were imported through grey customs clearance.